DC motor's speed control methods:

A DC motor's speed control methods can vary by varying flux, armature resistance, or applied voltage. Different speed control methods for different DC shunt and series methods are there. We also know that a DC motor is an electrical machine that converts direct current electrical energy into mechanical energy.
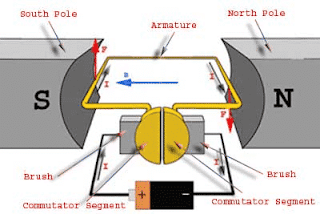
Brushes are placed within the North-South. North-South Poles of permanent or electromagnets when the current carrying armature is connected to the supply end through the commentator segment. Using these electromagnets' operating principle depends on Fleming's left-hand rule to determine the direction of the force acting on the armature conductors of the DC motor.
DC shunt motor is controlled methods by the stated below.
1) Flux control method
2) Armature and Rheostatic control method
3) Voltage control method
Voltage control methods are two types.
a. Multiple voltage control
b. Ward Leonard system
Flux Control Method. 

In this method, the speed of a dc motor is inversely proportional to the flux per pole. Thus, decreasing flux and speed can be increased and vice versa. To control the flux, the rheostat is added in series with the field winding will increase the speed, and because of this flux will decrease. So, the field current is relatively small and hence copper loss is decreased. This method is quite efficient.
Armature and Rheostatic control method.

The speed of a dc motor is directly proportional to the back E M F. That means, that when the supply voltage V and the armature resistance Ra are kept constant, speed is directly proportional to the armature current Ia. Thus, if we add a resistance in series with the armature, Ia decreases and, hence, the speed also decreases. The greater the resistance in series with the armature, the greater the decrease in speed.
Multiple voltage control.

In this method, the shunt field is connected to a fixed exciting voltage, and the armature is supplied with different voltages. The voltage across the armature is changed with the help of suitable switchgear. The speed is approximately proportional to the voltage across the armature.
Ward Leonard system.

This Ward - Leonard system is used where very sensitive speed control of the motor is required (e.g. electric excavators, elevators, etc.). The arrangement of this system is as required in this figure. In this method, the output from the generator G is fed to the armature of the motor M2 whose speed is to be controlled. The output voltage of the generator G can be varied from zero to its maximum value using its field regulator and, hence, the armature voltage of the motor M2 is varied very smoothly. Hence, very smooth speed control of the dc motor can be obtained by this method. Speed of DC Series motor is controlled methods by the stated below.
a. Flux control method
Flux control methods are four types.
1. Field diverter.
2. Armature diverter.
3. Trapped field control.
4. Paralleling field coils.
b. Variable Resistance in series with the armature.
c. Series -parallel control method.
Field diverter.

A veritable resistance is a connected parallel to the series field. This variable resistor is called a diverter, as the desired amount of current can be diverted through this resistor, and hence current through the field coil can be decreased. Hence, flux can be decreased to the desired amount and speed can be increased.
Armature diverter.

Diverter or Rheostat is connected across the armature. For a given constant load torque, if armature current is reduced then flux must increase. This will result in an increase in current taken from the supply and hence flux will increase and subsequently speed of the motor will decrease.
Tapped field control.

The field coil is tapped dividing the number of turns. Thus we can select the different values of flux by selecting different numbers of turns. Paralleling field coils. In this method, several speeds can be obtained by regrouping coils.
Variable Resistance In Series With armature. 

Introducing a resistance in series with the armature can reduce the voltage across the armature. And, hence, speed reduces in proportion with it.
Series Parallel Control. 

This system is widely used in electric traction, where two or more mechanically coupled series motors are employed. For low speeds, the motors are connected in series, and for higher speeds, the motors are connected in parallel. When in series, the motors have the same current passing through them, although voltage across each motor is divided. When in parallel, the voltage across each motor is the same although the current gets divided.
Thank You
